Tomato and cherry tomato harvesting robot
Tomato and cherry tomato harvesting robot

Fig.1 shows a tomato and cherry tomato harvesting robot. This robot consists of 4 components; manipulator, end-effector, visual sensor, and traveling device. Here, those components are described. A seven degrees of freedom manipulator was used to harvest larger size tomato and cherry tomato fruits as shown in Fig.1 (Kondo et al., 1993; 1994c; 1995a). This manipulator could have high manipulatability when it had a harvesting posture. The manipulator consisted of two prismatic joints and five rotational joints. The lengths of upper arm and fore arm were 250 mm and 200 mm, while strokes of the prismatic joints are 200 mm in horizontal direction and 300 mm in vertical direction.
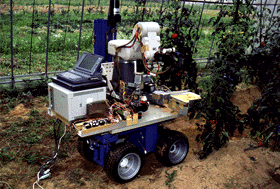
Fig.1 Tomato harvesting robot.
As harvesting end-effectors, two types have been developed; one is for larger size tomato fruit (Monta et al., 1994, Fig.2) and the other is for cherry tomato fruit (Fig.3). The former one had two fingers with a suction pad. The pad is able to suck a fruit pneumatically to separate it from the fruit cluster by the pad moving backward in the end-effector, because several fruits had adjacent positions one another and stems were also closed to the cluster sometimes. The end-effector for cherry tomato could suck a fruit into the end-effector pneumatically by a blower connected with the end-effector. When the fruit took an appropriate position in the end-effector, its peduncle was nipped around its joint by nipper closing. If the fruit was not at the position, the manipulator moved the end-effector's position back or forth until photo-interrupters told the appropriate position of fruit. The harvested fruit was transported to a container through tube between the end-effector and the container (Kondo et al., 1995e). A color CCD camera could be used to discriminate both fruits from their stems and leaves based on R, B, and G components, because matured tomato fruits had red color (Kondo et al., 1996c). The positions of the fruits were able to be detected basically by binocular stereo vision. A four wheel type traveling device which could travel in the ridge automatically was used for mounting the robot. This kind of traveling device was already commercialized as a vehicle for transporting in greenhouse. We are going to propel a project for a new tomato harvesting robot with a university in USA, an electrical company and an institute of agricultural machinery (Kondo et al., 1997b).
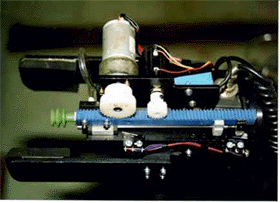
Fig.2 Larger size tomato harvesting end-effector
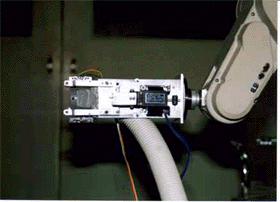
Fig.3 Cherry tomato harvesting end-effector.
Tomato and cherry tomato harvesting robot
Cucumber harvesting robot
Strawberry harvesting robots
Multi-operation robot for grapevine
Safety system for agricultural robot
Chrysanthemum cutting sticking robot
Weed Detection in lawn field
Plant diagnosis system
Quality Evaluation for agricultural products
List of Recent English Publications in Laboratory of Agricultural Systems Engineering
Menu page
Top page (English)
Top page (Japanese)




